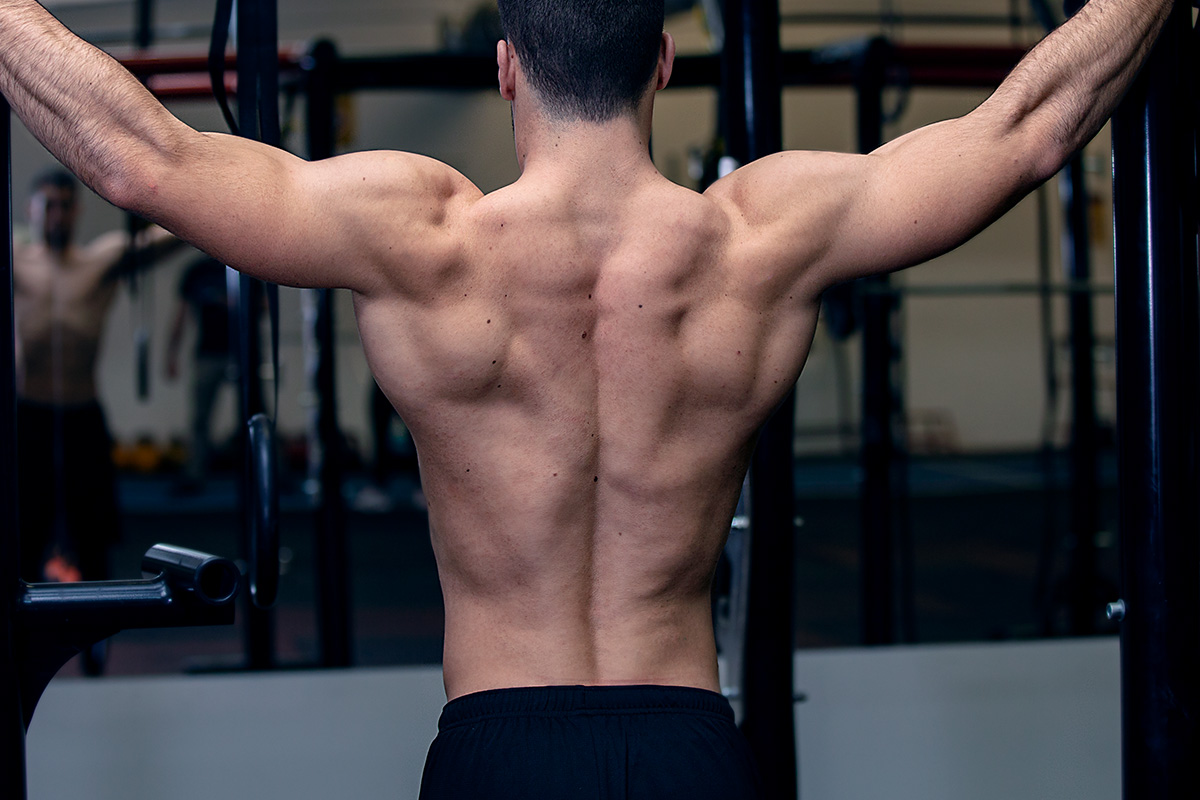
Back muscles play a vital role in posture, movement, and stability, and understanding their anatomy and function is crucial for maintaining a healthy back. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of back muscles, providing insights into their structure, function, and how to strengthen and care for them.
Regular exercise is widely regarded as the most effective means of preventing flexibility issues. Studies have shown that regular physical activity helps to maintain and improve range of motion in the joints, muscles, and connective tissues, such as back muscles . By engaging in regular stretching and strengthening exercises, individuals can enhance their overall flexibility, reducing the risk of injuries and improving their physical performance.
Back muscles are divided into several groups, including the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and erector spinae. Each muscle group has a unique origin, insertion, and function, contributing to the overall strength and mobility of the back.
Anatomy of Back Muscles
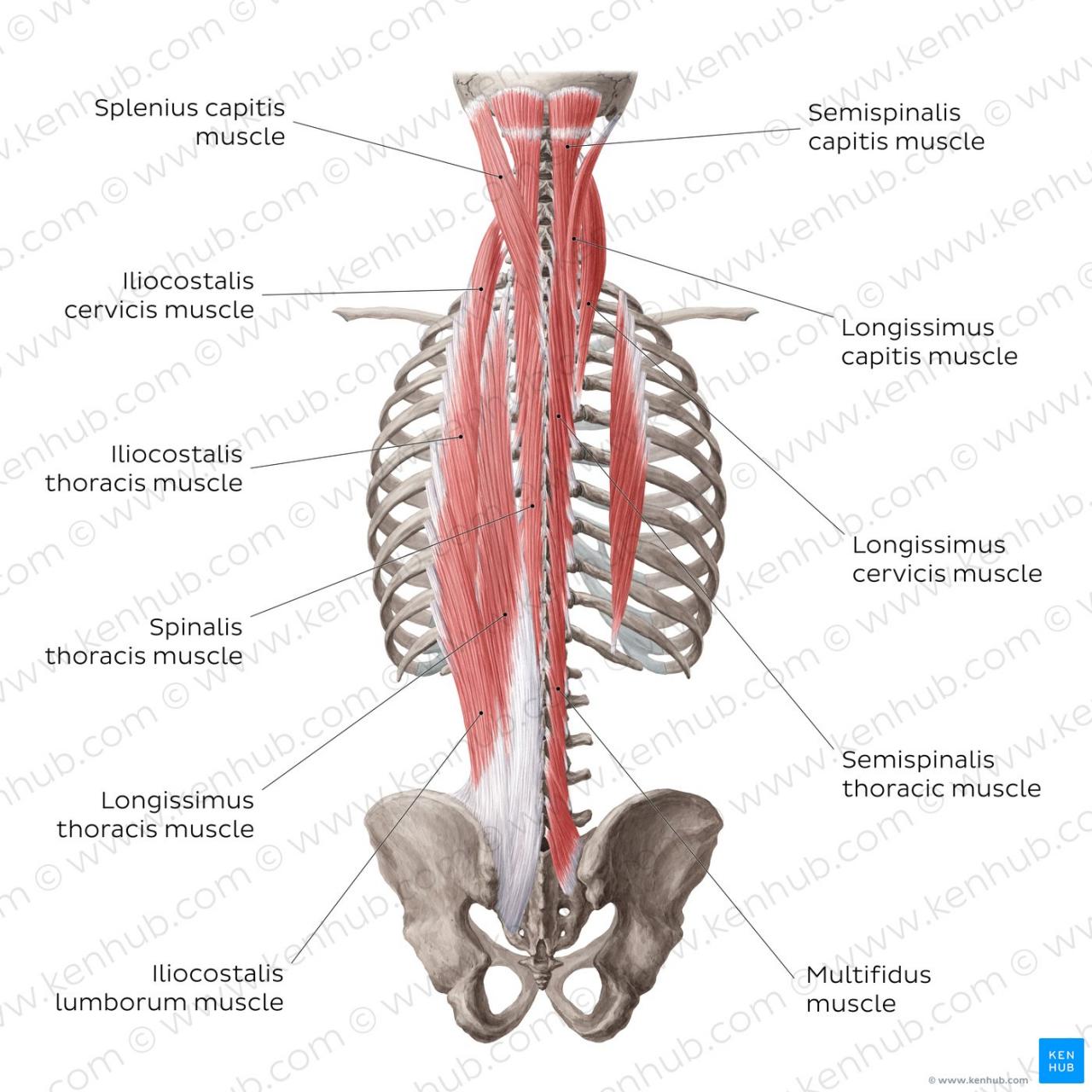
The back muscles, also known as the dorsal muscles, are a complex group of muscles that cover the posterior aspect of the body. They play a crucial role in supporting the spine, maintaining posture, and facilitating movement.
Major Back Muscle Groups, Back muscles
- Superficial muscles:These muscles lie closest to the skin and include the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and rhomboids.
- Intermediate muscles:These muscles are located beneath the superficial muscles and include the erector spinae, multifidus, and rotatores.
- Deep muscles:These muscles are located deepest and include the transversospinalis, interspinales, and intertransversarii.
| Muscle Group | Origin | Insertion | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trapezius | Occipital bone, cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae | Clavicle, acromion, scapula | Elevation, retraction, and rotation of the scapula |
| Latissimus dorsi | Lumbar vertebrae, iliac crest, lower ribs | Humerus | Adduction, extension, and internal rotation of the arm |
| Rhomboids | Cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae | Scapula | Retraction and elevation of the scapula |
| Erector spinae | Sacrum, lumbar vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae | Vertebrae | Extension of the spine |
| Multifidus | Sacrum, lumbar vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae | Vertebrae | Rotation and extension of the spine |
End of Discussion: Back Muscles
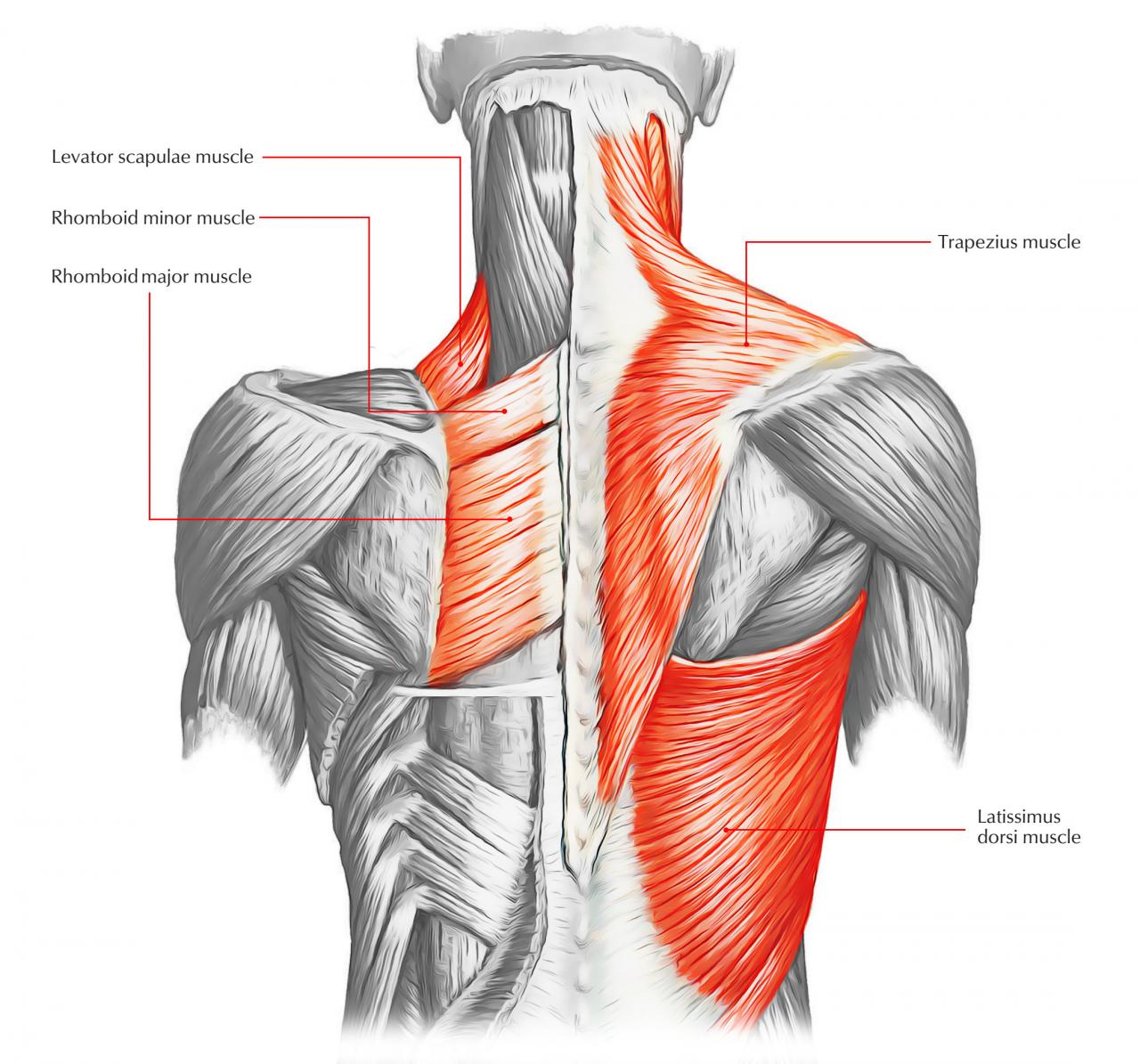
By understanding the anatomy and function of back muscles, individuals can develop effective workout plans to strengthen them, reduce the risk of injuries, and improve overall back health. Regular stretching and massage techniques can further enhance flexibility and reduce tension in the back muscles, promoting a healthy and pain-free back.
Regular exercise is the key to maintaining flexibility and preventing stiffness in the body. By engaging in regular physical activity, you can improve the range of motion in your joints and keep your muscles supple. This is especially important for older adults, as flexibility issues can become more prevalent with age.
According to experts , regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles that support your joints, such as the back muscles and the hamstrings . It can also help improve your posture and balance, which can reduce your risk of falls and injuries.
Popular Questions
What are the most common back muscle injuries?
Strains, sprains, and herniated discs are among the most prevalent back muscle injuries.
How can I prevent back muscle injuries?
Maintaining good posture, practicing proper lifting techniques, and engaging in regular exercise can help prevent back muscle injuries.
What are the benefits of stretching back muscles?
Stretching back muscles improves flexibility, reduces tension, and helps prevent injuries.
